Table des matières
Loading demo files or your own data
Synchronous and asynchonous temporal formats
DataTube2 considers its own two CSV formats for temporal data:
- The synchronous temporal format is when all data attributes (i.e., variables) were recorded at the same time steps and with the same temporal difference between time steps. Hence, it is a matrix, like in this example:
| Time step | Variable1 | Variable2 |
|---|---|---|
| 2003-09-28 00:00:00 | 10 | 15 |
| 2003-09-29 00:00:00 | 12 | 15 |
| 2003-09-30 00:00:00 | 14 | 12 |
If you use the synchronous format, be sure that the two above conditions are met.
- The asynchronous temporal format considers that data attributes were recorded at any time and independently. This is an “event” type representation, like in this example:
| Time step | Variable name | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 2003-09-28 00:00:00 | Variable1 | 10 |
| 2003-09-29 00:30:00 | Variable1 | 15 |
| 2003-10-01 00:00:00 | Variable1 | 13 |
| 2003-09-29 01:30:00 | Variable2 | 15 |
| 2003-11-01 00:00:00 | Variable1 | 13 |
This array does not need to be sorted.
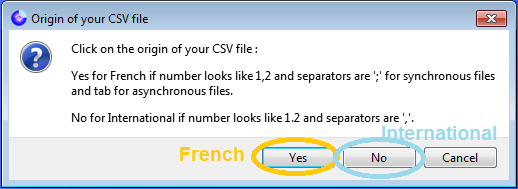
CSV format for synchronous files: French (separator = ";", decimal =",") or International (separator = ",", decimal = ".")
To begin, let us remind you that the differences between the French CSV format and the International CSV format are the following:
| French CSV format | International CSV format | |
|---|---|---|
| Cell separator | ; | , |
| Decimal separator | , | . |
The DataTube2 synchronous format supports both encodings. To open a synchronous file, please start with:
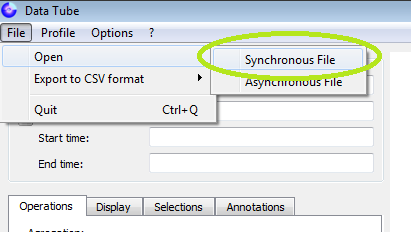 and then specify the French/International encoding by answering “Yes” or “No” in the following window, which is diplayed when you open a file:
and then specify the French/International encoding by answering “Yes” or “No” in the following window, which is diplayed when you open a file:
CSV format for asynchronous files: International (separator = "TAB", decimal = ".")
The asynchronous format in DataTube2 uses TAB character as separator and “.” for decimals. To open an asynchronous file, please select:
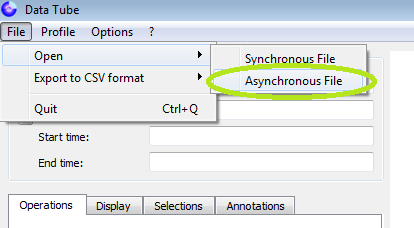
and then:
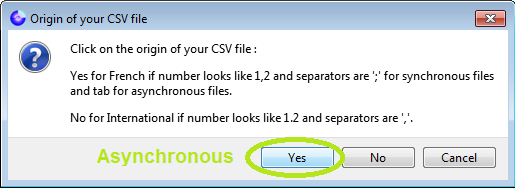
Loading and visualizing the demo files
Simple demo files with artificial data are provided in each format (synchronous or asynchronous). For the synchonous format, we give you some examples for each CSV encoding (French or international).
As an example, here are the first lines of file “DT2-synchronous-small-file-french.csv”, which is synchronous and with the French CSV encoding:
Time,VAR1,VAR2,VAR3,VAR4,VAR5,VAR6,VAR7,VAR8,VAR9,VAR10, …
timestamp,numeric,numeric,numeric,numeric,numeric,numeric,numeric,numeric,numeric,…
3;;;;;;;;;;…
4;;;;;;;;;;…
5;;;;;;;;;;…
6;;;;;;;;;;…
7;;;;;;;;;;…
8;;;;;;;;;;…
9;;;;;;;;;;…
10;;;;;;;;;;…
2003-09-28 00:00:00;-1000;15,1;81,1;35;14;213;0;6;25;14;…
2003-09-29 00:00:00;34;13;75;34,15;153;1;7;35;15;…
…
Here are the first lines of file “DT2-synchronous-small-file-international.csv”, which is synchronous and with the International CSV encoding:
Time,VAR1,VAR2,VAR3,VAR4,VAR5,VAR6,VAR7,VAR8,VAR9,VAR10, …
timestamp,numeric,numeric,numeric,numeric,numeric,numeric,numeric,numeric,numeric,…
3,,,,,,,,,,…
4,,,,,,,,,,…
5,,,,,,,,,,…
6,,,,,,,,,,…
7,,,,,,,,,,…
8,,,,,,,,,,…
9,,,,,,,,,,…
10,,,,,,,,,…
2003-09-28 00:00:00,-1000,15.1,81.1,35,14,213,0,6,25,14,…
2003-09-29 00:00:00,34,13,75,34,15,153,1,7,35,15,…
…
Finally, here is a sample of an asynchronous file, which is asynchronous with TAB separators:
VAR1 2006-02-01 00:00:00 310.1
VAR1 2006-02-02 00:00:00 320
VAR1 2006-02-03 00:00:00 330
VAR1 2006-02-04 00:00:00 340
VAR1 2006-02-05 00:00:00 350
…
Encoding your own data
To encore your own data in a CSV file:
- Select the format to use, i.e., either synchronous or asynchronous (see explanations above),
- Study the examples provided with DataTube2 (see the Data directory),
- Give names to the variables,
- To represent time values :
- the GMT format is yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss
- yyyy must be greater than 1970 (this is due to the EPOCH format, we'll try to improve this in future releases),
- DataTube2 can use GMT or EPOCH (but yet, please use GMT, we need additional testing for EPOCH format),
- To represent data values:
- for synchronous format (see the discussion above), use either the French CSV format (like this “;3,1415;”) or the International CSV format (like this “,3.1415,”),
- for asynchronous format, use TAB for separators and “.” for decimals,